Norton’s theorem:
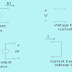
Norton's theorem in Any two-terminal linear bilateral dc network can be replaced by an equivalent circuit consisting of a current source and a parallel resistor,
Thevenin’s theorem with respect to the equivalent circuit can also be applied to the Norton equivalent circuit. The steps leading to the proper values of IN and RN are now listed.
3. Calculate RN by first setting all sources to zero (voltage sources are replaced with short circuits and current sources with open circuits) and then finding the resultant resistance between the two marked terminals. (If the internal resistance of the voltage and/or current sources is included in the original network, it must remain when the sources are set to zero.) Since RN = RTh, the procedure and value obtained using the approach described for Thevenin’s theorem will determine the proper value of RN
4. Calculate IN by first returning all sources to their original position and then finding the short-circuit current between the marked terminals. It is the same current that would be measured by an ammeter placed between the marked terminals.
5. Hence,Draw the Norton equivalent circuit with the portion of the circuit previously removed replaced between the terminals of the equivalent circuit.
5. Hence,Draw the Norton equivalent circuit with the portion of the circuit previously removed replaced between the terminals of the equivalent circuit.





No comments:
Post a Comment